Tag: Jordan
An opportunity that may be missed
The Middle East is in a rare period of rapid change. The Assad regime in Syria is gone. Its successor is still undefined and uncertain. Israel has crippled Iran’s Hamas and Hizbollah allies. It is trying to do likewise to the Houthis in Yemen. Egypt is on the sidelines, preoccupied with civil wars in Libya and Sudan. A weakened Iran is contemplating whether nuclear weapons would help to restore its regional influence.
The global powers that be are not anxious to get too involved. Russia, stretched thin, let Syria go. The United States is inaugurating a president known to favor withdrawal from Syria. He will support almost anything Israel wants to do. China is doing its best to guarantee access to Middle East oil but wants to avoid political involvement. The European Union has a similar attitude.
So what will be the main factors in determining the future of the Middle East? Who has power and influence in the region and outside it?
Turkiye
The Turks are so far the big winners in Syria. They are getting an opportunity to send back Syrian refugees and will try to decimate their Syrian Kurdish enemies. They have influence over the ruling Hayat Tahrir al Sham (HTS) leadership in Damascus, whom they supplied and unleashed.
When it comes to reconstruction in Syria, Turkish companies are experienced and nearby. Turkish pockets aren’t as deep as American or Chinese pockets. But they are deep enough to get things started fast, especially if World Bank money is put on the table.
The Turks will try to convince the Americans to leave. They’ll argue that they can and will suppress Islamic State and other terrorists. They may even promise to allow the Kurds to continue their local governance structures. But they would want the Syrian Kurds to cut their ties to Kurdish terrorists inside Turkey.
The Turks will want a not-too-Islamist government in Damascus, something akin to their own. Syria has an enormously diverse population. HTS governance in Idlib was autocratic. But that was during the civil war. It will be much harder to impose that on Damascus after liberation from Assad. Syrians want their freedom. Turkiye has an interest in their getting it. Only inclusive governance will permit the return of refugees.
The Gulf
Some of the big money for reconstruction in Syria will come from the Gulf. The Saudis may be willing, if they gain some political influence in the bargain. How they use that influence will be important. In the Balkans 30 years ago they sponsored Wahabist clerics and mosques. Mohammed bin Salman has marginalized those within Saudi Arabia. We can hope he will not export them now. But he will, like the Turks, want a strong executive in Damascus.
What Syria needs from the Gulf is support for inclusive, democratic governance. The UAE will weigh in heavily against Islamism, but the Emirates are far from democratic or inclusive. Qatar, more tolerant of Islamism, will prefer inclusion, if only because the Americans will pressure them to do so.
Israel
Prime Minister Netanyahu has not achieved elimination of Hamas in Gaza. But he has weakened it. The Israelis have been far more successful in Lebanon, where they have dealt heavy blows to Hezbollah. They are also destroying many Syrian military capabilities. And they have seized UN-patrolled Syrian territory in the Golan Heights and on Mount Hermon.
Israel had already neutralized Egypt and Jordan via peace agreements. Ditto the UAE and Bahrain via the Abrahamic accords, though they were never protagonists in war against Israel. It would like similar normalization with Saudi Arabia. Now Israel controls border areas inside Lebanon and Syria. Repression on the West Bank and attacks on the Houthis in Yemen are proceeding apace.
Netanyahu is resisting the end of the Gaza war to save his own skin from the Israeli courts and electorate. Whether he succeeds at that or not, his legacy will be an “Israeli World.” That is a militarily strong Israel surrounded by buffer zones. But he has done serious damage to Israeli democracy and society.
Iran
Iran is weakened. That will encourage it to quicken the pace of its nuclear program. It won’t go all the way to deploying nuclear weapons. That would risk giving the Israelis an excuse for a massive attack, or even a nuclear strike. Nor can Ankara adopt the Israeli policy of opaqueness, as it is a signatory of the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty. That requires openness to inspections. So transparency about its nuclear threshold status is the likely policy.
Bottom line
Turkiye, Israel, and the Gulf (especially Saudi Arabia) are the big winners from the current Middle East wars. They would be even stronger if they were to cooperate. All have an interest in preventing Iran from getting nuclear weapons, in stabilizing Syria, and in preventing terrorist resurgence. So does the US. There is an opportunity, but one that may be missed.
Getting to Syria’s next regime
The fall of the Assad regime in Syria was swift. Now comes the hard part: building a new regime that is an improvement. We know from past experience some of the elements required. Let’s review those, in light of the discussion among Syrians above.
Safe and secure environment
Above all, a safe and secure environment free of large-scale violence is a prerequisite.
The biggest threat for now is in the north. Turkish and Turkish-supported forces there are pressing hard against Kurdish and Kurdish-led forces. Turkiye President Erdogan wants the Kurds east of the Euphrates and at least 30 kilometers from the border. An American-mediated truce between the Turks and the Kurds has broken down. There is a real risk of a major conflict between them. Turkiye says its objective is eliminating the Kurdish forces. But Ankara and its allies don’t seem to make much distinction between specific Kurdish forces and Kurds iin general.
In other parts of the country there are also risks. It would be a mistake to assume that Assad did not organize “stay behind” forces. Even if not organized, they may emerge spontaneously, or Islamic State sleeper cells may awaken. In Iraq, the Saddam Fedayeen originated the insurgency against the American occupation that the Islamic State continued. There is still the possibility of revenge killings. A single mass grave near Damascus apparently holds 100,000 bodies. That means close to one million people with motives for seeking revenge.
Unifying the many armed groups under the new Syrian government will be a major challenge and priority. HTS has announced its intention to do this. But it will need to convince rebel leaders and find the resources to pay the fighters. Eventually it will need to demobilize many of them and integrate them into civilian life.
Rule of law
While there was some looting of government offices in Damascus, most Syrians have maintained law and order. Hayat Tahrir al Sham (HTS), the leading force in the revolution, has kept police and government officials in their positions. Opposition forces in the south and other parts of the country have done likewise. There has been no sign, yet, of widespread revenge killings.
It will be years before Syria can reform its laws. In the meanwhile, there are urgent issues. Perhaps first among them is establishment and protection of property rights. In Idlib, HTS had a serious system for property issues. Expanding that to the national level will be a major challenge. Without that, it will be hard even to start reconstruction. According to the World Bank and the European Union, Syria has suffered an enormous amount of infrastructure damage. In 14 cities, they estimate damages of $8.7-11.4 billion.
Syria’s judicial sector was not independent of the Assad regime. It did what it was told. Judges and prosecutors will need to be vetted and new ones trained and named. Prison officials and guards will need to be likewise vetted and many replaced. Lawyers will need to be trained and retrained.
Accountability will be a priority. Identifying those responsible for Assad regime abuses will be easy at the top levels. But most of those people will have fled. Europe and the US need to be alert for their entry and capture them sooner rather than later. At the lower levels, many perpetrators will try to melt into the general population. It will be difficult to ferret them out and put them on trial quickly. Doing so will take years of concerted effort. It is not easy to gather the evidence a serious jury trial requires.
Stable governance
While Assad’s Syria conducted elections and had a parliament, it operated as an autocracy. The Assad family, the Ba’ath party, and Alawite military officers were pillars of the regime. It showed no respect for the rights of others. The new regime should reflect what Rafif calls a core commitment to human rights, including freedom of expression and religion. The mantra today is “inclusion,” which ultimately will require political pluralism, including full participation of women and minorities.
That will not be easy. HTS is also an autocratic organization, with little respect for women’s equality and dubious commitment to equal rights for minorities. It has appointed an interim government with little “inclusion” and has been less than clear about the role of women.
Political parties and civil society organizations are emerging quickly, but elections are still far off. It may be possible and desirable to convene a national dialogue of notable citizens. Russia and Iran, the foreign mainstays of the Assad regime are calling for one. Choice of participants would of course be problematic. But a national dialogue may provide common ground not only for Syrians but also for international powers interested in Syria.
Ultimately Syria will need a new constitution. Lots of constitutional proposals already exist. But Syria will need a constituent assembly of some sort to draft a democratic and inclusive document. Many of the issues involved have been discussed, but difficult choices lie ahead.
In the meanwhile, local governance will need to suffice. Syrians have practiced it a good deal in opposition-held areas in recent years. It won’t be a bad place to start.
Sustainable economy
Syrians are destitute. Their most immediate needs are food and fuel. Humanitarian assistance should flow as soon and as quickly as possible. This means using the United Nations and international relief organizations, which are already overburdened by Gaza and Lebanon.
Going much beyond humanitarian relief will require relief from sanctions and de-designation of HTS as a terrorist group. This will take time and convincing. The Americans and Europeans will want to be sure they are not snookered. They won’t want to provide reconstruction assistance to a new regime that fails to meet reasonable criteria. The big money will come from the World Bank and the Gulf. Washington and Brussels control the former and influence the latter.
Assad’s regime was dependent on production and trade of Captagon, an amphetamine. That will have to stop. HTS will crack down hard, but it will need also to generate economic opportunities to replace the drug trade. Syria is a country with limited oil and gas resources, big agricultural and tourism potential, and a good geographic location. Where its future livelihood will come from is unclear. Like Jordan and Egypt, it will need international assistance for decades into the future.
The World Bank has found that disruption of social networks has caused most of the economic damage in Syria. Restoring trust will take time and effort.
Social well-being
Half of Syria’s population is either refugees or displaced within the country. Many will want to return home. Others will not. Compensation for destroyed or expropriated property will be a major issue. Some communities will never return to their pre-war composition. Others will want to make an effort to do so.
The health system in Syria has imploded. Even in areas where the Russians and Syrian did not attack hospitals, sanitary supplies and equipment are limited. Many doctors and nurses have fled. Technical capabilities are not up to modern standards. Rebuilding will be a major enterprise.
The education system still functions in most of the country. Children go to school in both government and opposition controlled areas. But many buildings are destroyed and students will be behind in learning. Efforts were made to keep the education system in some opposition-controlled areas compatible with Syrian government requirements. But the culture of the schools and the experience of the students will be dramatically different.
The international dimension
Syria now faces two main challenges from neighbors. One is the Turkish effort to destroy the Kurdish institutions in the northeast. The other is the effort to destroy the strategic assets of the Syrian Arab Army, which Israel is bombing. Additionally, Israel has seized a UN-patroled buffer zone on the Golan Heights. HTS leadership is not prepared to fight Israel, even though some of its cadres would like to do so. HTS wants to bring the Kurdish institutions under Damascus authority. The Kurds are amenable. They do not advocate independence or union with the Kurds in Iraq. But Turkiye has vowed to try to destroy the Kurdish institutions. This is a serious threat and could vastly complicate the post-war situation.
Russia appears to be withdrawing much of its military assets from Syria. Iran has already done so. The US for now is maintaining its troops in support of the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces. The Americans will want to withdraw, but will not do so before Donald Trump takes office in January. What he will do is not clear.
United Nations Security Council resolution 2254 (2015) is still the main international community statement on political transition in Syria. It is not a bad one.
For now, Netanyahu is succeeding
Israel’s air force is destroying Syria’s navy, weapons manufacturing sites, chemical and other weapons depots. It is undertaking hundreds of sorties per day. The Israel Defense Force (IDF) has also seized control of the UN buffer zone on the Golan Heights. That was created in a 1974 agreement.
Location, location, location
None of this should be surprising. Syria for the moment can’t defend itself. Its longtime enemy is trying to weaken it further. Among many other advantages, Israel now occupies the peak of Mount Hermon. That has unimpeded electronic visibility over a good part of Syria, including the capital, and Lebanon. This is valuable real estate.
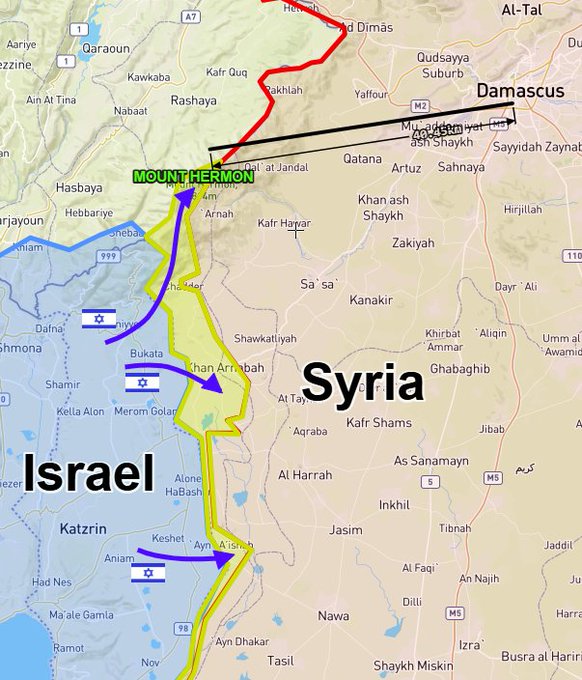
The Israelis can do this because the Syrian Arab Army has disintegrated and the Russians are not preventing it. While Assad was in power, Israel raided Syrian sites, but only with a wink and a nod from Moscow. Now it is unclear whether Moscow has no objection or is simply unwilling or unable to object. Syrian and Russian air defenses have not reacted to the Israeli attacks.
The American position
Former President Trump formally proclaimed in 2019 that the United States recognizes the Golan Heights as “part of Israel.” The Biden administration upheld that policy with a 2021 tweet. It is hard to picture Trump in a second term reversing it. He has signaled, not least with appointment of an evangelical Christian as ambassador, that he will back Israel. Even more than Biden did.
That does not necessarily mean the United States will want Israel to hold on to the UN buffer zone. But Netanyahu will no doubt press Trump hard on that issue. In the past, Trump has given the Israeli Prime Minister pretty much everything he has asked.
The new Syrian government has its hands full
Hayat Tahrir al Sham (HTS) has named Mohammed al Bashir as interim prime minister until March 1. He was the head of the Syrian Salvation Government (SSG). That is the government HTS empowered for several years in the territory it controlled in the northwest province of Idlib. Al Bashir and SSG officials have met with President Assad’s outgoing officials to arrange the transfer of responsibilities. This is far more orderly than one might have anticipated. Let’s hope it can continue that way. Syria’s economy and population need relief. Those are for now top priorities.
But no Syrian leader will fail eventually to claim all of the Golan Heights. Some HTS fighters have declared their next objective is Jerusalem. Their leader’s nom de guerre is Abu Mohammed al Jolani (more or less father of Mohammed of Golan). Least of all one whose parents came from there. Al Jolani’s father was an Arab nationalist and supporter of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). Al Jolani himself says the second intifada radicalized him. Netanyahu will no doubt be hearing from him in due course.
But al Jolani has his hands full for the moment. Turkish-backed forces are attacking US-backed Kurdish forces in northern Syria. Al Jolani wants the Kurds to support the new regime. Turkiye President Erdogan, an important HTS backer, wants them pushed away from the Turkish border and east of the Eurphrates. That’s east of Manbij on the map below. The Turkish/Kurdish conflict could explode and weaken the unified effort HTS has tried to construct.

The broader picture
Syria would be weak in the present situation even if the Israelis weren’t contributing to its travail. But Netanyahu’s policy is to burn down his neighbors’ houses. He has done it in Gaza, Lebanon, and now Syria. He would no doubt like to do the same in Yemen. Jordan is already a client state, as the monarchy owes its continued existence to Israeli security cooperation. Egypt is likewise neutralized, even if uncomfortable with Israel’s behavior in Gaza. Netanyahu’s aim is a regionally hegemonic Greater Israel. He wants full control over the West Bank and Gaza and cowed enemies in Lebanon and Syria. For now, he is succeeding.
Winners and losers from Assad’s fall
The success of Syrians in deposing Bashar al Assad poses the question of who wins and who loses. Inside Syria, Hayat Tahrir al Sham is the big winner for now. It led the breakout from Idlib and inspired the many risings elsewhere in Syria.
There are lots of other countries that stand to win or lose something in the transition. Let’s assume Syria remains reasonably stable and its government basically inclusive and not vindictive, which appears to be HTS’ intention. We can try to guess the pluses and minuses for the rest of the world.
Turkiye is the big winner
In the region, Turkiye is the big winner. President Erdogan had been ready to negotiate with Assad, who refused to engage. Erdogan lost patience and backed a military outcome. He unleashed both Turkish proxies and HTS, which could not have armed and equipped itself adequately without Ankara’s cooperation. He does not control HTS 100%, especially now that it is in Damascus. But he will have a good deal of influence over its behavior. Let’s hope he uses it in the democratic and less religious direction. That however is the opposite of what he has been doing at home.
Erdogan has two primary goals in Syria. First is achieving enough stability there to allow many of the three million Syrian refugees in Turkiye to return. Returns will take time, but there is already a spontaneous flow back into Syria. The second is keeping the Syrian Kurds associated with the Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK) away from Turkiye’s border with Syria. Erdogan would also like its Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES) dissolved. Or at least as far from power as possible.
Refugee returns look like a good bet. Disempowering the Kurds in eastern and northern Syria does not. They are well-established and cooperate closely with US forces in that area. Future President Trump will want to withdraw the Americans. But the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces will remain essential to fighting the Islamic State (IS). HTS, IS, and the PKK all carry the “terrorist” label in the US and Europe. But HTS and IS are rivals. HTS will want the Kurds to continue to fight IS. They will also be vital, at least temporarily, to preventing Iran from re-establishing a land route through Syria to Lebanon.
Israel wins and loses
The Israeli government would have preferred to see the Assad devil it knew stay in power. But his fall means the Iranians and their proxies will no longer be stationed along the northeastern border of Israel. The Israelis have already moved their troops into a UN-patrolled buffer zone inside Syria. They didn’t want some known or unknown force filling that vacuum. That advance might give them a stronger position in future negotiations with Damascus, whenever those occur.
But Israelis have to be worried that a jihadist group led the overthrow of Assad. Ahmed al Sharaa, the birth name of HTS’s Abu Mohammed al Jolani, was born in Riyadh to Syrian parents. They were displaced from the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights. The second Palestinian intifada motivated his conversion to jihad. It is hard to picture someone with that background more pliable than the impacable Assad on border and Palestinian issues. Jolani himself appears to have said little about Gaza or the Lebanon war. But some of his followers are clear about where they want to go next:
Lebanon and Jordan
Lebanon and Jordan, two key neighbors of Syria, can hope to be winners from the change of regime . Both will want to see Syrian refugees return home, as they were a strain on their economies. They will also stand to gain from reconstruction and eventually a more prosperous Syria.
Assad had been financing his government and his cronies with proceeds from the export of the stimulant Captagon. Decent people in both Beirut and Amman will welcome relief from that flood of poison into and through their societies. Some of their corrupted politicians may regret it.
Lebanon will have to reabsorb Hezbollah fighters who supported Assad. They will be a defeated and unhappy lot. But the Lebanese Army and state stand to gain from any weakening and demoralization of Hezbollah. Anyone serious in Beirut should see the current situation as an opportunity to strengthen both.
Iran and Russia are the biggest losers
Apart from Assad, Tehran and Moscow are the biggest losers. They backed Assad with people, force, money, and diplomacy. They are now thoroughly discredited.
Iran has already evacuated its personnel from Syria. Tehran has lost not only its best ally but also its land route to Lebanon.
Russia still has its bases. Almost any future Syrian government will have a hard time seeing what it gains from the Russian air force presence. Moscow’s air force brutalized Syrian civilians for almost 10 years. The air bases will no longer have utility even to Moscow. Moscow will prioritize keeping the naval base at Tartus, which is important for its Mediterranean operations.
The Gulf gains, Iraq loses
Gulf diplomacy was trying to normalize relations with Assad in the past year or two. But few Gulfies will mourn his regime, provided stability is maintained. Qatar may be more pleased than Saudi Arabia or Abu Dhabi. The Saudis and Emiratis are less tolerant of political Islam. Nor do they like to see regimes fall. Qatar is more comfortable with political change, including of the Islamist variety.
Iraq’s Shia-dominated government loses a companion in Damascus. It won’t welcome a Sunni-dominated government in Damascus. But Baghdad, like the Gulf, is unlikely to mourn the fall of Assad. He did his damnedest to make life difficult for Iraqis after the fall of Saddam Hussein.
The United States and Europe gain but will need to ante up
The US and Europe have long viewed Assad as a regrettable but necessary evil. They hesitated to bring him down for fear of what might come next. Now they need to step up and fund Syria’s recovery, mainly through the IMF and the World Bank. They will want Gulf money invested as well. The best way to get that is for them to ante up matching funds.
That is also the best way for them to gain leverage over the political settlement. If they want an inclusive outcome, they’ll need to be ready to pay for it. Hesitation could open the door to malicious influence.
Let the Syrians decide
That said, the details of the political settlement should be left to the Syrians. They will need to write a new constitution and eventually hold elections. The extensive constitutional discussions the UN has hosted for a decade may offer some enlightenment on what Syrians want. Just as important in my view is how the new powers that be handle property issues. Only if property rights are clearly established and protected can Syria’s economy revive. But who rightfully owns what and what to do about destroyed property are complicated and difficult issues.
The regional war is likely to intensify


With Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu about to address the US Congress, it is time for an assessment of where things stand currently in the Middle East. Israel is fighting Arab opponents on four fronts. In Gaza, it is fighting Hamas and killing a lot of civilians. In the north, Israel is fighting Hizbollah and sometimes Syria. In the south Yemen’s Ansar al Allah (the Houthis in a word) has taken up the cudgels against Israel and shipping in the Red Sea. And on the West Bank, settlers and the security forces are fighting Palestinian civilians.
Iran stands behind it all
Iran supports all of Israel’s opponents, the “axis of resistance,” in the Middle East and North Africa. It supplies training and equipment as well as some degree of central coordination and financing. Hamas, Hizbollah, the Houthis may each have their own interests and initiatives, but they are broadly consistent with Iran’s denial of the legitimacy of the Israeli state and its objective of destroying it in favor of a one-state solution on the entire territory of Palestine.
From Tehran’s perspective, the fighting is a good deal. It is confronting its sworn enemy using non-Iranian forces not on Iranian territory. Only once, in April, has Iran tried to attack Israel with its own missiles and drones, in response to an attack on an Iranian diplomatic facility. Israel responded, but in a way that did not escalate the direct tit for tat.
The fourth front
The fourth front in the current fighting is the West Bank. There Israel is not only fighting armed resistance, some of which might or might not be connected to Iran. It has unleashed Israeli settlers, who are establishing new outposts, destroying Palestinian property, and killing Palestinians. 2023 was an especially bad year but 2024 is not far off the pace.
The West Bank fighting redounds to Iran’s benefit as well. It keeps Israeli security forces busy and makes it difficult for the Palestinian Authority, a secular organization with little connection to Tehran, to claim it can effectively govern.
Arab states are mostly maintaining the peace
Egypt and Jordan are maintaining their peace agreements with Israel. Saudi Arabia is continuing to pursue a similar accommodation, albeit one that would necessarily open a path to a Palestinian state. It would also need to give Saudi Arabia a formal US security guarantee of some sort. Iraq talks tough but is not either willing or capable of joining the fight. Turkey has suspended trade with Israel and speaks up for the Palestinians, but it is unwilling to go further. Bahrain, Morocco, and Sudan are more or less maintaining their “Abrahamic” agreements with Israel, though Khartoum may rethink that after its civil war.
Qatar is acting as a mediator, along with Egypt, in talks that engage both Hamas and Israel. While often accused of supporting Hamas, Doha views its relations with Hamas as fulfilling requests of the US government, as does Cairo. Egyptian President Sisi is no friend of the Muslim Brotherhood, which gave birth to Hamas.
Hamas has survived, many hostages haven’t
The immediate cause of the current fighting was Hamas’ ferocious, unconventional attack on Israel last October 7, which killed about 1200 people. Israelis understood that to be an existential threat. Its ferocious conventional response has killed in the past 8 months about 40,000 Palestinians and others, according to the Hamas health ministry.
Israel’s main objective is to eradicate Hamas’ military and governing capabilities. Hamas appears to have survived the intense bombing campaign and numerous ground incursions. While there are signs of dissatisfaction with Hamas among Gazans, polling has not confirmed that sentiment.
Israel also seeks release of hostages seized on October 7. Netanyahu claims military pressure will achieve that. Many Israelis prefer a deal. Hamas or other Palestinian groups still hold about 120. More than 100 were released in exchange for Palestinian prisoners held in Israel. Few have been rescued. Dozens have been killed.
No agreement means the regional war will intensify
Prime Minister Netanyahu, apparently against the wishes of many in his government, has refused to sign on to a proposed ceasefire agreement with Hamas that the Americans say originated with Israel. Hamas claims to have agreed, but it appears to be asking for changes as well. There is no sign of a real agreement emerging.
Many in Israel wanted Netanyahu to sign on before coming to Washington. He did not do that. It seems unlikely he will sign on during his visit, if only because doing so would help the Democrats. Netanyahu has allied himself firmly with Donald Trump. I expect his address in Congress to be more of the same fire and brimstone that he preaches in Israel.
The result will be more fighting in all four directions. The Houthis are unbowed. Lebanese Hizbollah is less belligerent but will have little choice if Israel continues to kill its commanders. Hamas hopes its continuing resistance will give it traction not only in Gaza but also on the West Bank, where the settlers can be expected to continue rampaging.
Hamas reportedly agreed in Beijing this week to join the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), recognizing it as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people (a key provision of the Oslo accords with Israel). Such reconciliation agreements have not stuck in the past. If this one does, it could put the Palestinians in a better position to negotiate with Israel, or it could incentivize the Israelis to continue the fighting. Or both. Stay tuned.
The wider war has arrived, when will peace?
Iran yesterday retaliated against Israel for its bombing of the Iranian consulate in Damascus, which killed high ranking officers of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. The barrage of hundreds of drones and missiles was ineffective, due to Israeli, American, British, and Jordanian air defenses. The Iranians made no secret of what they intended to do and presumably are hoping it will not trigger another round.
Multiple vectors
But it is still reasonable to conclude that the wider Middle East war many have feared has already begun. Israel continues its attack on Gaza. Lebanese Hizbollah and Israel are exchanging shots across the border. Israel is frequently targeting Iranian assets in Syria. Yemen’s Houthis are targeting shipping and warships in the Red Sea. Iraq’s Iranian-sponsored “Popular Mobilization Forces” have been targeting American military bases. Israeli settlers have been chasing Palestinians from their homes on the West Bank.
Of course the pace and lethality of this wider war could heighten. So far, its most deadly axis by far has been Israel/Hamas. Hamas has killed about 1500 Israelis and the Israelis have killed tens of thousands of Palestinians, in retaliation for the mass murder, kidnapping, and mayhem of October 7. Elsewhere the wider war is more than symbolic, but still far less fatal.
Worsening prospects
Once such things start, the natural tendency is towards escalation. Certainly things have gotten worse in the past six months. They are likely to get worse still. The murder of an Israeli teenager on the West Bank last week sparked heightened settler violence against Palestinians there. Hizbollah could do a lot more damage if it unleashes its missiles. So could the Israelis if they decide to push into southern Lebanon. Iran still has lots of drones and missiles it could use in a second attack.
The next round will be Israel’s choice. It could choose to write off yesterday’s attack as ineffective and unworthy of response. Or it could decide to reassert deterrence with a direct attack on Iran or on Iranian assets in the region. I suspect the decision will be based primarily on Prime Minister Netanyahu’s domestic political calculations. He faces growing demands for his resignation. Any pause in the fighting could provide the time to bring him down. He is still hoping for enough of a victory in Gaza, Lebanon, or Iran to enable him to remain in power.
That seems unlikely in Gaza. Israel has done significant harm to Hamas there but is still far from the total defeat Netanyahu has set as its war goal. Israel has been hitting Hizbollah in Lebanon without much reaction. That could be a likelier prospect. He may think a devastating blow against Iran would enable him to avoid the inevitable for a while longer. Why anyone in his war cabinet would go along with that is unclear to me, but so far they have generally supported his wartime decisions.
Can diplomacy work?
The still wider and more deadly war in prospect is not in the US interest. Nor do the Europeans want it. Karim Sadjadpour on MSNBC last night pointed out that the Chinese would likewise prefer stability in the Middle East to lower and steady oil prices. The Russians by contrast benefit from de-stabilization and the consequent distraction from the Ukraine war as well as the bump up in oil prices. But even acting together it is unclear that the Americans, Europeans, and Chinese could exert sufficient influence on Israel or Iran to de-escalate.
Both countries have leaders whose political mandates won’t last much longer. Iran’s Supreme Leader is almost 85 years old and ill. Netanyahu is suffering a catastrophic decline in popularity as well as serious corruption charges. Both are claiming not to want to escalate. But neither sees an enticing option other than escalation. Both want victory over the other as a political legacy. The wider war has arrived, but until there is decisively new leadership in both Tehran and Jerusalem peace is unlikely.




 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
