Tag: United States
Make Putin watch his back
Alexander Vindman is the former National Security Council official who gave vital incriminating testimony in Trump’s first impeachment. He blew the whistle on the President’s phone call with President Zelensky of Ukraine, in which Trump sought dirt on then candidate Joe Biden. Now a doctoral student at SAIS, Vindman has interesting, if discouraging, things to say about Russian intentions with respect to Ukraine:
Not a lot of good options in Ukraine
Vindman believes Russia is likely to invade Ukraine, with the aim of keeping Ukraine in its sphere of influence and making it a failed state, one that cannot offer a democratic model for those who want to escape Moscow’s tentacles. Sanctions he thinks won’t have much more impact than in the past, because Russia has hardened its economy against them. In addition, Putin controls a $620 billion sovereign wealth fund, and China will help cushion the blow.
The best military hope lies in NATO countries. The US could station more troops in NATO countries near Ukraine. They, especially those on the eastern front that Russia threatens, could in turn train the Ukrainians and perhaps deploy troops and equipment to help the Ukrainian army defend against attack.
But Putin is vulnerable elsewhere
Vindman ignores Putin’s vulnerabilities beyond Ukraine. One of these was dramatically apparent in Kazakhstan over the last few days, when protesters challenged President Tokayev. The protests quickly turned violent. Tokayev sought Russian help to protect vital installations and ordered his forces to shoot to kill.
The Russians did not send a big force–supposedly only 2500 troops–but Putin is also saddled with defending his annexation of Crimea, besieged Belarusan President Lukashenko, secessionist provinces in Georgia, and the homicidal Syrian President Assad, not to mention maintaining Russian forces in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Tajikistan, and Kyrgyzstan. The Russians are also active through proxy forces in Libya and the Central African Republic. They are building bases in half a dozen African countries. Russian empire-building is reaching further than even Moscow’s Soviet-era ambitions.
A crisis in any one of these places could bring a halt to Putin’s ambitions in Ukraine.
Including at home
Putin is also vulnerable at home. While he has acquired de facto autocratic powers, he is less popular than once he was. Corruption is his Achilles heel. The Kremlin has murdered one potential rival and poisoned, then imprisoned, another. A free and fair election could well do Putin in, so he won’t allow that. He also faces local ethnic and religious minority resistance to his increasingly nationalist and chauvinist rule.
If the Americans want to protect Ukraine, they will need not only to beef up its defenses and undermine Russia’s economy, but also figure out how to exploit Putin’s political and military vulnerabilities beyond Ukraine.
Make Putin watch his back.
This is the Bosnia we should support
I have added my name to this appeal, published today:
We are writing to you on behalf of the friends of Bosnia and Herzegovina who have gathered on 10 January 2022 in Brussels, London, Ottawa, Toronto, Geneva, Oslo, Rome, Stockholm, Gothenburg, Vienna, Sarajevo and many other cities all around the world to express our utmost concern about the current political and security crisis in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
In October 2021 the ruling coalition in the Bosnian and Herzegovinian entity of Republika Srpska (RS) adopted a plan to create what it called “an independent RS within the Dayton Bosnia and Herzegovina.” A seven-page long document laid out concrete steps for unilateral, illegal and unconstitutional takeover of state-level competences in fiscal, judicial, defence, security and many other areas. This plan is available in public and among other points, foresees use of force against any state-level institution that would try to defend the constitutional order of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The implementation of the plan will cause collapse of the constitutional and institutional architecture of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It will result in terrible political, economic and security consequences. With several concrete steps already taken, the ruling coalition in the RS has made it clear that it intends to implement its plan.
On 10 December 2021 the RS Assembly adopted four conclusions on the so-called “transfer of authorities” and one so-called “declaration on constitutional principles” by which the RS legislative body has de facto and de jure decided to remove this entity from the state constitutional and legal system of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the sectors of judiciary, defense and security and indirect taxation. Moreover, the RS assembly has tasked and empowered the RS government to draft new entity laws on: the RS army, RS intelligence service, RS indirect taxation system and RS high judicial and prosecutor council as well as more than 130 other laws and necessary regulations in various sectors by which RS will abolish and replace the respected state laws and regulation with entity ones.
As neither the state or RS entity constitution, nor state or entity laws allow any possibility for the entity institutions to issue legally valid decisions or laws on matters which are already imposed and regulated by state constitution or laws, the above-mentioned actions and decisions of RS assembly from 10 December 2021 are an illegal usurpation of state power and a criminal act against state constitutional and legal order.
By October 2021 the RS adopted and published in Official Gazette the unconstitutional entity law, which abolished the validation of the state-level law prohibiting genocide denial in the scope of RS. On 28 December 2021, another unconstitutional law was published in the Official Gazette. This Law on the RS Agency for medicinal products and devices could, as the European Commission noted in its recent letter to the RS authorities, lead to a collapse of the medicinal market and deprive citizens of basic medicine.
This crisis in Bosnia and Herzegovina has nothing to do with inter-ethnic relations; it is an artificial crisis provoked by corrupt nationalists and their partners. They do not have the support of the opposition in the RS Assembly, nor of the majority of the citizens of Bosnia and Herzegovina, including those living in the RS.
The country has now been drawn into a political crisis that threatens peace and a meaningful, robust and coordinated response by the High Representative of the International Community, Christian Schmidt himself, United Nations, United States, the European Union and its NATO allies is required.
A lack of such response so far has only served to embolden Mr. Dodik’s and his ruling coalition’s ambitions. Particularly worrying are statements by government officials in Serbia, who have expressed their support for the plan of ruling coalition in RS. Alongside this, the RS secessionists enjoy the bolstering support of Russia, China and even some EU member states such as Hungary whose open nationalism, xenophobia and anti-Muslim sentiment is very much rampant.
Instead of pushing back, some in international community are only encouraging Mr. Dodik’s aspirations for secession and desire to undermine and eventually destroy Bosnia and Herzegovina as a sovereign state. However, there are very serious reasons why Bosnia and Herzegovina needs not only to be preserved as a sovereign state but also further strengthened.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a specific cultural entity that has existed for more than 1000 years, where citizens of different ethnic origins and religious traditions have lived together for centuries.
Even today, despite the war in the 1990s, a large number of citizens accept the existence and legitimacy of the state of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The 2019 European Values Study showed that 74 per cent of the population is proud of having Bosnian and Herzegovinian citizenship. This sentiment is the strongest in the Brcko District (88 per cent), while in RS 66 percent share this view.
Neither the peace agreement nor the constitution provide for the right of secession. It would be a disastrous historic precedent if the ‘entity’ whose political and military leaders (as well as its army and police) have been convicted for severe war crimes and genocide, with over one million people expelled, were ‘granted’ independence.
In the past 26 years, the EU and its Member States, the USA and other countries of the world, and many international organizations have invested a lot of political, diplomatic, human and financial resources in effort in maintaining peace and rebuilding the country. Bosnia and Herzegovina’s citizens, Croats, Bosniaks, Serbs, Jews, Romas, and all those Bosnians who do not identify themselves with a specific ethnic group, want to live in peace and harmony, nurtured by democracy.
On 10 January 2022, Bosnians and Herzegovinians of all ethnicities and religions, atheists and agnostics, together with their friends from all around the world will gather in Brussels, Geneva, London, Vienna, Oslo, Ottawa, Toronto, Rome, Stockholm, Sarajevo and many other cities across the world to stand for united Bosnia and Herzegovina, for its pluralism, coexistence and preservation and to issue following demands to the High Representative of the International Community, Christian Schmidt, as well as to the European Commission and the governments of the United States, United Kingdom, European Union Member States and NATO allies:
- The plan adopted and currently implemented by the ruling coalition in the Bosnian and Herzegovinian entity of Republika Srpska should be recognised as an attack on the long-lasting peace, constitutional order, sovereignty, territorial integrity and 30-year independence of Bosnia and Herzegovina and as a threat to peace, stability and security in the Western Balkans and Europe.
- A meaningful, robust and coordinated response should be developed and implemented as a matter of priority with a primary focus on deterring the local forces of destabilization and foreign mentors, and then focusing on constructive and reformative approaches. This response should include a mix of interventions, starting with sanctions and strengthening of the NATO/EUFOR military presence as a clear political signal.
- Support domestic institutions in their response to the attack on the constitutional order of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Foremost, by providing full support to the Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina to review the two laws already passed, and all other that might be passed by the RS Assembly. Furthermore, by providing political and technical support for the state-level judiciary to investigate the attack on the constitutional order of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
- Recent statements and activities by high-ranking officials of the government of Republic of Serbia are violating the principle of good neighbourly relations, which are at the heart of the EU accession talks and a violation of the Stabilisation and Association Agreement between the EU and Serbia. EU Member States should consider suspension of accession talks with Serbia unless its government changes its position towards Bosnia and Herzegovina, including that related to the 1990’s war crimes and genocide.
Stevenson’s army, January 8
[FYI, I’ll be away for a few days]
-SecState Blinken says US has two new security arrangements with Japan. There was more in his Friday news conference.
-WH denies report of troop cuts in Europe.
– Bloomberg reports on bureaucratic fights over cyber.
– Vox reports on former Trump officials.
– Atlantic Council has several reports on 2022 foreign policy issues.
My SAIS colleague Charlie Stevenson distributes this almost daily news digest of foreign/defense/national security policy to “Stevenson’s army” via Googlegroups. I republish here. To get Stevenson’s army by email, send a blank email (no subject or text in the body) to stevensons-army+subscribe@googlegroups.com. You’ll get an email confirming your join request. Click “Join This Group” and follow the instructions to join. Once you have joined, you can adjust your email delivery preferences (if you want every email or a digest of the emails).
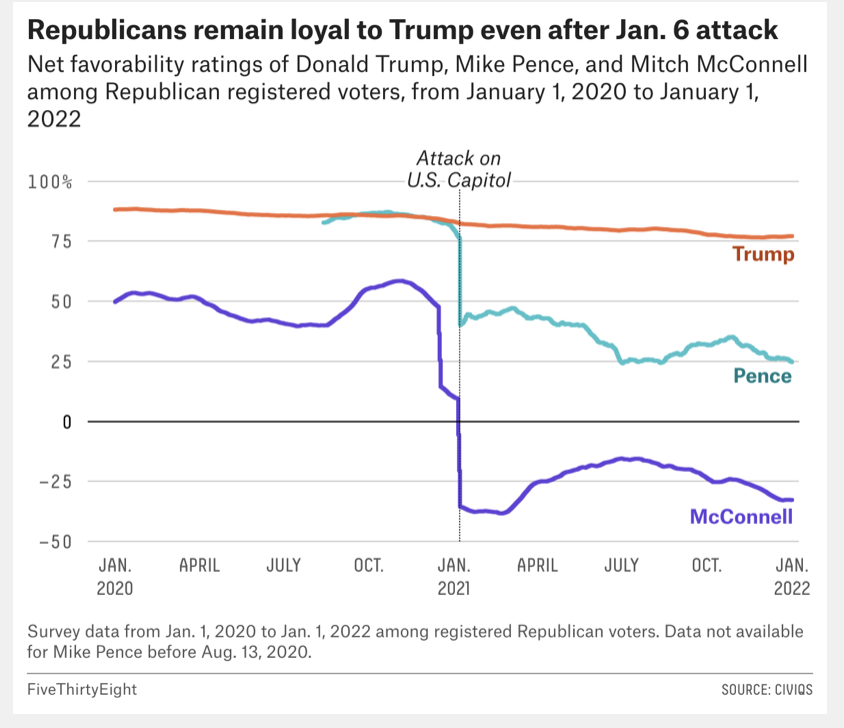
It should never have come to this
Donald Trump lost the election fair and square, as confirmed in court and every respectable recount and audit. His incitement of the January 6 riot disgraced him. The House impeached him for it, for the second time. And there is a good chance New York State will indict him for tax evasion and other financial crimes. Richard Nixon didn’t come close to this before resigning.
But he is in charge
But Trump is also in charge of the Republican Party. Or shall I say the Republic Party, to imitate its adherents’ shortening of the Democratic Party’s name. It has certainly lost something. The GOP is no longer grand or old. It has departed from fiscal conservatism. It views face masks and social distancing as tyranny. President Lincoln, who suspended habaeus corpus during the Civil War, would find that hard to fathom. And the Republic Party is responding readily to Donald Trump’s racist dog whistles, now audible to everyone.
Then yesterday the Republicans failed to show up at the commemorative events. They thus aligned themselves with the Trump-inspired and -encouraged rioters who attacked The Capitol a year ago to block a constitutionally mandated process. Or more accurately: all but Liz Cheney and her father (!) failed to show up. Denying the events the respect they deserved, the Republicans then accused the Democrats of partisanship. This is Donald Trump’s Republican Party: devoted to polarization, big lies, and violence against American institutions.
The test is nigh
Only a few months remain before this new version of the Republican Party chooses its 2022 candidates for Congress and one-third of the Senate. With Trump in charge, they will be people to his liking. In the many Republican strongholds, that won’t matter, as their election is ensured. But in some “battleground” districts and states citizens will have a serious choice between Trumpistas who mouth his fantasies and people firmly grounded in reality. The 2022 election is going to tell us a lot about whether America can escape the Trump stain on its history.
Americans have a choice. They can revert to the politics of polarization, exclusion, and fantasy. Or they can opt for reality, inclusion, and democracy. Even posing the alternatives is saddening. It should never have come to this.
PS:
Sanctions for destabilizing and corrupt activity
The US Treasury’s announcement today of sanctions on Milorad Dodik and Alternativna TV merits reprinting in full. I don’t expect this will have any immediate effect on Dodik or his TV station, both of which presumably anticipated it. Dodik probaby does most of his personal business in cash anyway. The TV station may have some trouble with international transfers. But more importantly this decision will have a PR and psychological effect. It is a clear and unequivocal signal that the United States wants Dodik gone and a warning to those politicians who support his destabilizing activities. The impact will be greater if European Union member states join in:
WASHINGTON — Today, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) designated Milorad Dodik (Dodik), who is a member of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH), as well as one entity under his control, Alternativna Televizija d.o.o. Banja Luka, in response to Dodik’s corrupt activities and continued threats to the stability and territorial integrity of BiH.
Today’s action, the first designations under E.O. 14033, builds on the Biden Administration’s commitment to promote accountability for those who, among other things, undermine the stability of the Western Balkans region through corruption and threats to long-standing peace agreements. Dodik has undermined BiH institutions by calling for the seizure of state competencies and setting in motion the creation of parallel institutions in BiH’s Republika Srpska (RS) entity. Furthermore, Dodik has used his official BiH position to accumulate personal wealth through graft, bribery, and other forms of corruption. His divisive ethno-nationalistic rhetoric reflects his efforts to advance these political goals and distract attention from his corrupt activities. Cumulatively, these actions threaten the stability, sovereignty, and territorial integrity of BiH and undermine the Dayton Peace Accords, thereby risking wider regional instability.
“Milorad Dodik’s destabilizing corrupt activities and attempts to dismantle the Dayton Peace Accords, motivated by his own self-interest, threaten the stability of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the entire region,” said Under Secretary of the Treasury for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence Brian E. Nelson. “The United States will not hesitate to act against those who pursue corruption, destabilization, and division at the expense of their own people, as well as against those who enable and facilitate this behavior.”
DODIK’S DESTABILIZING AND CORRUPT ACTIVITIES
The Dayton Peace Accords (DPA), signed by the Presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, and Serbia in 1995, brought an end to ethnic conflict in BiH and established the present-day constitution of BiH. Treasury previously designated Dodik on January 17, 2017, pursuant to E.O. 13304, for having actively obstructed or posed a significant risk of actively obstructing the DPA. Today’s actions build on this legacy by targeting his ongoing destabilizing activity with respect to the DPA, as well as his abuse of his official position to engage in widespread corruption, which undermines state institutions in BiH.
Dodik has also openly called for, and has taken action toward, the unilateral transfer of state competencies from the BiH government to the Republika Srpska (RS), one of two entities that comprise BiH along with the Brcko District. Dodik has also publicly opposed the internationally appointed High Representative for BiH and the composition of the BiH Constitutional Court. Additionally, Dodik has publicly denigrated other ethnic and religious groups within BiH, further sowing division and political gridlock. Dodik, therefore, is being designated pursuant to E.O. 14033 for being responsible for or complicit in, or having directly or indirectly engaged in, a violation of, or an act that has obstructed or threatened the implementation of, the DPA.
Dodik is also being designated pursuant to E.O. 14033 for being responsible for or complicit in, or having directly or indirectly engaged in, corruption related to the Western Balkans. Specifically, he has established a patronage network in BiH from which he and his associates benefit. As one example of his corrupt actions, Dodik has provided government contracts and monopolies in the RS directly to close business associates. With his corrupt proceeds, Dodik has engaged in bribery and additional corrupt activities to further his personal interests at the expense of citizens in the RS.
DODIK’S PERSONAL MEDIA STATION
Alternativna Televizija d.o.o. Banja Luka (ATV), a media outlet based in Banja Luka, RS, is privately owned by a company closely linked to Dodik’s family. However, Dodik himself exerts personal control over ATV behind the scenes, such as by requiring personal approval on media stories related to politically sensitive topics. Dodik acquired ATV to deliberately and expressly further his own agenda, which includes his efforts to denigrate other political figures, burnish his public image, and advance his own personal and political goals.
Dodik has awarded ATV-related contracts directly to members of his family, which he has used as yet another avenue for corruption. He has funneled money directly from public companies to ATV for corrupt purposes. Dodik has substantially increased funding for ATV in recent years and engaged in malign social media influence campaigns through ATV to publish content that advances his political and personal goals.
ATV is being designated pursuant to E.O. 14033 for being owned or controlled by, or having acted or purported to act for or on behalf of, directly or indirectly, Dodik.
SANCTIONS IMPLICATIONS
As a result of today’s action, all property and interests in property of the individual and entity above that are in the United States or in the possession or control of U.S. persons are blocked and must be reported to OFAC. In addition, any entities that are owned, directly or indirectly, 50 percent or more by one or more blocked persons are also blocked. Unless authorized by a general or specific license issued by OFAC, or exempt, all transactions by U.S. persons or within (or transiting) the United States that involve any property or interests in property of designated or otherwise blocked persons are generally prohibited. The prohibitions include the making of any contribution or provision of funds, goods, or services by, to, or for the benefit of any blocked person, or the receipt of any contribution or provision of funds, goods, or services from any such person.
For identifying information on the individual and entity designated today.
Voting rights can cure the fantasy
The prevailing wisdom these days is that America is polarized. Accordng to PBS, Democrats and Republicans are living in alternate realities. Both see the threat to democracy as real, but coming from two different directions. The implication: we need to come together and heal our deep divides before something even worse than the January 6 attack on the Capitol happens.
This is nonsense
We are not living in alternate realities. Some of us are living a fantasy. They think Biden stole the election, that COVID-19 is not a big problem, and that public health requirements infringe on their freedom. They deny that the January 6 riot was a riot, that Trump incited it, or that Trump supporters were violent.
None of this is true. The evidence is plain. No one has demonstrated election fraud capable of affecting the outcome of the 2020 election. COVID has killed more than a million Americans. Wearing a mask and social distancing are not the equivalent of the Nazi requirement that Jews wear a yellow star and live in ghettoes and concentration camps. January 6 was a violent insurrection Trump encouraged to block consitutionally-mandated certification of the election results. The courts have already convicted 75 of the miscreants and are prosecuting hundreds more.
The fantacists among us are lying, not putting forward an alternate hypothesis.
The “other side” is firmly based on reality. Biden was elected in accordance with the Constitution. Stemming the epidemic requires vaccination, masks, and social distancing. Trump’s supporters stormed the Capitol on January 6 and violently tried to block a constitutionally mandated procedure.
There is no doubt about these things. Fantasy is not an alternate reality.
The question is why?
Why would people choose a fantasy, one they know the facts do not support?
The main purpose is to consolidate identity. To be a Republican these days, you have to say you believe at least parts of the fantasy. That’s what holds the party together. It has no coherent governing proposals. It was not only unable to formulate an alternative to Obamacare but also abandoned fiscal conservatism during four years in the White House. Under Biden Republicans helped pass a giant infrastructure spending bill, but now oppose his social spending bill on fiscally conservative grounds.
Republicans now have an identity, one that its adherents can be relied upon to sustain, however flimsy its contact with reality. That identity is tightly entwined with white supremacy. The dog whistling about election fraud is all about tacitly claiming that black people can’t be trusted to count votes. The opposition to sensible public health measures originated when Americans thought the epidemic was mostly affecting black people and other minorities. The January 6 rioters were good people, as they were overwhelmingly white and Trump supporters.
Voting rights are the only cure
January 6 was a violent protest against a shift in demographic power. America is no longer as dominated as once it was by whites who alternate politely in power. It is doubtful whether any Republican can win a majority of the popular vote. Only one (George W) has done so, once, since 1992. Biden’s Electoral College margin was the same as Trump’s when he beat Hillary Clinton. But Biden ran 7 million votes ahead of Trump, even though Trump ran millions of votes ahead of his own popular vote count in 2016.
The January 6 rioters know this. Those who enouraged the riot also know that the Electoral College and the Senate favor less populous, more Republican states. And they know that state legistures, according to the Constitution, have the power to determine how Electoral Votes are cast, even if all have long since decided to do it in accordance with the popular vote. Republicans control more state legislatures, which are busy trying to restrict voting, get rid of non-partisan election officials, and open the possibility of determining themselves how the Electoral Votes will be case, no matter the popular vote outcome.
The only cure is national voting rights legislation, not “coming together.” If it forces Republicans to compete fairly in 2022 and 2024, they will see the need to drop the dog whistling and lying. They might even return to their former role as fiscal conservatives. Senate Majority Leader Schumer had better not be bluffing in promising limits on the anti-democratic filibuster, which has so far prevented passage, by January 17.
Remember January 6 for what it was: an attempted coup against a democratically elected President. Make sure it can’t happen again. Voting rights can cure fantasy.




 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
