Tag: Yemen
An opportunity that may be missed
The Middle East is in a rare period of rapid change. The Assad regime in Syria is gone. Its successor is still undefined and uncertain. Israel has crippled Iran’s Hamas and Hizbollah allies. It is trying to do likewise to the Houthis in Yemen. Egypt is on the sidelines, preoccupied with civil wars in Libya and Sudan. A weakened Iran is contemplating whether nuclear weapons would help to restore its regional influence.
The global powers that be are not anxious to get too involved. Russia, stretched thin, let Syria go. The United States is inaugurating a president known to favor withdrawal from Syria. He will support almost anything Israel wants to do. China is doing its best to guarantee access to Middle East oil but wants to avoid political involvement. The European Union has a similar attitude.
So what will be the main factors in determining the future of the Middle East? Who has power and influence in the region and outside it?
Turkiye
The Turks are so far the big winners in Syria. They are getting an opportunity to send back Syrian refugees and will try to decimate their Syrian Kurdish enemies. They have influence over the ruling Hayat Tahrir al Sham (HTS) leadership in Damascus, whom they supplied and unleashed.
When it comes to reconstruction in Syria, Turkish companies are experienced and nearby. Turkish pockets aren’t as deep as American or Chinese pockets. But they are deep enough to get things started fast, especially if World Bank money is put on the table.
The Turks will try to convince the Americans to leave. They’ll argue that they can and will suppress Islamic State and other terrorists. They may even promise to allow the Kurds to continue their local governance structures. But they would want the Syrian Kurds to cut their ties to Kurdish terrorists inside Turkey.
The Turks will want a not-too-Islamist government in Damascus, something akin to their own. Syria has an enormously diverse population. HTS governance in Idlib was autocratic. But that was during the civil war. It will be much harder to impose that on Damascus after liberation from Assad. Syrians want their freedom. Turkiye has an interest in their getting it. Only inclusive governance will permit the return of refugees.
The Gulf
Some of the big money for reconstruction in Syria will come from the Gulf. The Saudis may be willing, if they gain some political influence in the bargain. How they use that influence will be important. In the Balkans 30 years ago they sponsored Wahabist clerics and mosques. Mohammed bin Salman has marginalized those within Saudi Arabia. We can hope he will not export them now. But he will, like the Turks, want a strong executive in Damascus.
What Syria needs from the Gulf is support for inclusive, democratic governance. The UAE will weigh in heavily against Islamism, but the Emirates are far from democratic or inclusive. Qatar, more tolerant of Islamism, will prefer inclusion, if only because the Americans will pressure them to do so.
Israel
Prime Minister Netanyahu has not achieved elimination of Hamas in Gaza. But he has weakened it. The Israelis have been far more successful in Lebanon, where they have dealt heavy blows to Hezbollah. They are also destroying many Syrian military capabilities. And they have seized UN-patrolled Syrian territory in the Golan Heights and on Mount Hermon.
Israel had already neutralized Egypt and Jordan via peace agreements. Ditto the UAE and Bahrain via the Abrahamic accords, though they were never protagonists in war against Israel. It would like similar normalization with Saudi Arabia. Now Israel controls border areas inside Lebanon and Syria. Repression on the West Bank and attacks on the Houthis in Yemen are proceeding apace.
Netanyahu is resisting the end of the Gaza war to save his own skin from the Israeli courts and electorate. Whether he succeeds at that or not, his legacy will be an “Israeli World.” That is a militarily strong Israel surrounded by buffer zones. But he has done serious damage to Israeli democracy and society.
Iran
Iran is weakened. That will encourage it to quicken the pace of its nuclear program. It won’t go all the way to deploying nuclear weapons. That would risk giving the Israelis an excuse for a massive attack, or even a nuclear strike. Nor can Ankara adopt the Israeli policy of opaqueness, as it is a signatory of the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty. That requires openness to inspections. So transparency about its nuclear threshold status is the likely policy.
Bottom line
Turkiye, Israel, and the Gulf (especially Saudi Arabia) are the big winners from the current Middle East wars. They would be even stronger if they were to cooperate. All have an interest in preventing Iran from getting nuclear weapons, in stabilizing Syria, and in preventing terrorist resurgence. So does the US. There is an opportunity, but one that may be missed.
A stronger American still fumbles
President Biden made a farewell appearance at the State Department yesterday. As a former Foreign Service officer, I’m of course delighted that he did this. It is especially important and timely because the Department now faces Donald Trump’s threat of loyalty tests and mass firings.
Biden’s understandably directed his remarks at justifying what his Administration has done on foreign policy. So how did he really do?
The bar was low
Certainly Biden can justifiably claim to have strengthened America’s alliances. The bar was low. Both in Europe and Asia the first Trump Administration had raised doubts. Allies could not depend on Washington’s commitment to fulfill its mutual defense obligations. Biden’s claim that compared to four years ago America is stronger because of renewed and expanded alliances is true. He is also correct in claiming he has not gone to war to make it happen.
The extraordinary strength of the American economy is an important dimension of this strength. Voters decided the election in part on the issue of inflation. But the Fed has largely tamed that and growth has been strong throughout. Manufacturing is booming, including vital semi-conductor production. Investment in non-carbon energy sources has soared. The defense industrial based is expanding.
Biden is also correct in asserting that America’s antagonists are worse off. Russia has failed to take Ukraine because of the US effort to gather support for Kyiv. Iran and its allies in Gaza, Lebanon, and Syria are weaker. Only the Houthis in Yemen are arguably stronger than four years ago.
China is facing serious domestic economic and demographic challenges. But I don’t know why Biden claims it will never surpass the US. On a purchasing power parity (PPP) basis, it already has, though obviously per capita GDP in China remains much lower.
Some claims gloss over big problems
Biden is rightly proud that there is no longer war in Afghanistan, but he glosses over the chaotic withdrawal. He also doesn’t mention the failure of the Taliban to keep its commitments.
He vaunts progress on climate change, but without acknowledging that the goal of keeping global warming below 1.5 degrees centigrade will not be met.
Biden talks about infrastructure in Africa. But not about its turn away from democracy, civil wars in Sudan and Ethiopia, and the unresolved conflict in Libya.
He urges that Iran never be allowed to “fire” a nuclear weapon. That is a significant retreat from the position that Iran should never be allowed to have one.
Biden mentions the impending Hamas/Israel ceasefire. But he says nothing about Israel’s criminal conduct of the war in Gaza. Nor does he blame Israel’s right-wing government for the long delay in reaching a deal.
Biden’s legacy
At the end, Biden seeks to bequeath three priorities to Trump: artificial intelligence, climate change, and democracy. He no doubt knows that Trump isn’t going to take the advice on climate or democracy. He might on artificial intelligence, as his Silicon Valley tycoons will want him to.
Sad to say, Biden’s legacy will lie in other areas. Fearful of nuclear conflict with Russia, he failed to give Ukraine all the support it needs to defeat Russia. He was reluctant to rein in Israel for more than a year of the Gaza war. He failed to stop or reverse the Iranian and North Korean nuclear programs. America is stronger than it was four years ago, but it has not always used that strength to good advantage.
For now, Netanyahu is succeeding
Israel’s air force is destroying Syria’s navy, weapons manufacturing sites, chemical and other weapons depots. It is undertaking hundreds of sorties per day. The Israel Defense Force (IDF) has also seized control of the UN buffer zone on the Golan Heights. That was created in a 1974 agreement.
Location, location, location
None of this should be surprising. Syria for the moment can’t defend itself. Its longtime enemy is trying to weaken it further. Among many other advantages, Israel now occupies the peak of Mount Hermon. That has unimpeded electronic visibility over a good part of Syria, including the capital, and Lebanon. This is valuable real estate.
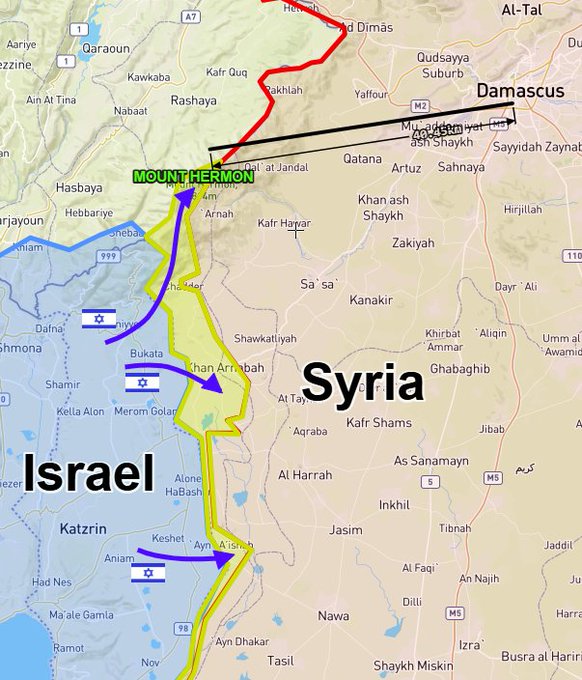
The Israelis can do this because the Syrian Arab Army has disintegrated and the Russians are not preventing it. While Assad was in power, Israel raided Syrian sites, but only with a wink and a nod from Moscow. Now it is unclear whether Moscow has no objection or is simply unwilling or unable to object. Syrian and Russian air defenses have not reacted to the Israeli attacks.
The American position
Former President Trump formally proclaimed in 2019 that the United States recognizes the Golan Heights as “part of Israel.” The Biden administration upheld that policy with a 2021 tweet. It is hard to picture Trump in a second term reversing it. He has signaled, not least with appointment of an evangelical Christian as ambassador, that he will back Israel. Even more than Biden did.
That does not necessarily mean the United States will want Israel to hold on to the UN buffer zone. But Netanyahu will no doubt press Trump hard on that issue. In the past, Trump has given the Israeli Prime Minister pretty much everything he has asked.
The new Syrian government has its hands full
Hayat Tahrir al Sham (HTS) has named Mohammed al Bashir as interim prime minister until March 1. He was the head of the Syrian Salvation Government (SSG). That is the government HTS empowered for several years in the territory it controlled in the northwest province of Idlib. Al Bashir and SSG officials have met with President Assad’s outgoing officials to arrange the transfer of responsibilities. This is far more orderly than one might have anticipated. Let’s hope it can continue that way. Syria’s economy and population need relief. Those are for now top priorities.
But no Syrian leader will fail eventually to claim all of the Golan Heights. Some HTS fighters have declared their next objective is Jerusalem. Their leader’s nom de guerre is Abu Mohammed al Jolani (more or less father of Mohammed of Golan). Least of all one whose parents came from there. Al Jolani’s father was an Arab nationalist and supporter of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). Al Jolani himself says the second intifada radicalized him. Netanyahu will no doubt be hearing from him in due course.
But al Jolani has his hands full for the moment. Turkish-backed forces are attacking US-backed Kurdish forces in northern Syria. Al Jolani wants the Kurds to support the new regime. Turkiye President Erdogan, an important HTS backer, wants them pushed away from the Turkish border and east of the Eurphrates. That’s east of Manbij on the map below. The Turkish/Kurdish conflict could explode and weaken the unified effort HTS has tried to construct.

The broader picture
Syria would be weak in the present situation even if the Israelis weren’t contributing to its travail. But Netanyahu’s policy is to burn down his neighbors’ houses. He has done it in Gaza, Lebanon, and now Syria. He would no doubt like to do the same in Yemen. Jordan is already a client state, as the monarchy owes its continued existence to Israeli security cooperation. Egypt is likewise neutralized, even if uncomfortable with Israel’s behavior in Gaza. Netanyahu’s aim is a regionally hegemonic Greater Israel. He wants full control over the West Bank and Gaza and cowed enemies in Lebanon and Syria. For now, he is succeeding.
Assassinations could mean war with Iran
Israel killed Fuad Shukr, military deputy to Hizbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah, in Beirut yesterday with a targeted air strike. Though they have not confirmed their involvement, the Israelis apparently also killed Ismail Haniyeh, political leader of Hamas in Tehran today, likely also with an air strike. There is I suppose some possibility that this was not their doing, but rather an Iranian maneuver due to displeasure with his leadership of Hamas, but that is 100% speculation.
The ultimate impact of these two assassinations, if such they be, is uncertain. Sometimes decapitation works. Sometimes it doesn’t. But the success of both operations tells us a good deal about Lebanon, Iran, and Israel.
Lebanon and Iran have weak air defenses
That Lebanon has ineffective air defenses is not surprising. The country has been on the ropes at least since the Beirut port explosion in 2020, but even before that its army could not match the Israelis on the ground or in the air. Lebanese Hizbollah is the main threat to Israel from the north. Its air defenses are improving. But the killing of Shukr demonstrates that Israel has the intelligence capability to track Hizbollah leadership and the precision strike capability to hit a single building in crowded southern Beirut without apparently activating either Lebanon’s or Hizbollah’s air defense.
The same is true, and even more impressive, for Iran, if in fact the Israelis did it. Haniyeh was killed in a residence facility of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). The Israelis would have had to track him there, evade Iranian air defenses, and strike accurately at a distance of almost 1000 miles from Jerusalem. Iranian inability to prevent this in the aftermath of the presidential inauguration yesterday suggests weak air defenses. Or a special forces unit might have penetrated on the ground.
Israel wants war with Iran
The Israeli willingness to undertake these two assassinations, if in fact Haniyeh was their doing, would suggest that Prime Minister Netanyahu is prepared to risk escalation of the already simmering regional conflict. The two assassinations may well provoke another direct attack from Iran, which tried and failed in April to punish Israel for an earlier Beirut assassination. Escalation this time could be rapid.
There is no question that Tehran backs Hamas, Hizbollah, and the Yemeni Houthis. This is the much-vaunted “axis of resistance,” whose leaders were in Tehran for the inauguration of a new president. Netanyahu earlier this month in his speech in Congress blamed Iran bluntly for their activities. He appears to want a direct confrontation with Tehran, rather than dealing only with its allies.
The Americans do not, but what they can do about it at this point is not clear. Netanyahu sees an opportunity to damage Israel’s enemies while the Arab states stand by. They too want to see Iran diminished. He likely figures the Americans will be pleased if Israel is successful. He appears little concerned with the possibility of failure.
Implications for the US
It will be hard for the US to stay aloof if Netanyahu is successful in provoking Iran into entering the regional war. The Middle East would once again have to take priority. Ukraine and China would have to wait. American military supplies to Israel would be vital.
An Israel/Iran war would likely affect the US presidential race. Kamala Harris would find Democrats divided. The aging leadership in Congress would want to back Israel. But many Democrats, like most Israelis, want Israel to end the war in Gaza by cutting a hostage deal with Hamas. Donald Trump would gain some advantage in the presidential race, even if his running mate has wanted to shift attention from the Middle East to the Pacific. American popular opinion will heavily favor Israel if there is war with Iran.
What’s missing from the Gaza peace plan
The Israeli proposal for “General Principles for an agreement between the Israeli side and the Palestinian side in Gaza on the exchange of hostages and prisoners and restoring a sustainable calm” in Gaza seems stalled, despite President Biden’s concerted efforts. What are its prospects?
Security, security, security
In real estate, it’s all about location, location, location. In post-war stabilization and reconstruction, it’s all about security, security, security.
The first security concern is that of the belligerents. They won’t agree to an end to the fighting if they think their own security will be at greater risk. This is especially true in the current case, as Israel has vowed to eliminate Hamas and Hamas’ strategic goal is the elimination of Israel. If Israel is responsible for security in Gaza after the ceasefire, Hamas has good reason to fear the Israel Defense Force will continue to target it, especially its leaders.
The second security concern focuses on civilians. The international community should not be interested in a ceasefire that fails to improve conditions for non-Hamas affiliated Gazans. They need not only to be housed and fed but also protected from gangs and chaos. That requires some sort of police force and rudimentary justice system. Without them, civilians have no recourse when a guy with a gun steals their food, water, shelter, and property.
The third security concern is the region. If war ends in Gaza only to start up between Lebanese Hizbollah and Israel, the Middle East will have gained little. The broader war the region has long feared is already brewing. Iran’s allies and proxies in Lebanon, Yemen, and Syria have all been attacking Israel. The missile and drone tit for tat between Iran and Israel in April suggested what a broader war might entail.
The gaping hole in the draft agreement
The peace plan lacks provisions for the first two categories of security. It details the time lines for hostage/prisoner exchanges, withdrawal of Israeli forces, humanitarian relief, return of Gazans to the north, and other requirements. But it refers only vaguely to Egypt, Qatar, and the US as “guarantors” of the agreement. That means little if it doesn’t include provision of security, or at least a leadership role in doing so.
But it is hard to see what those three countries can realistically do about security. Whoever does that will need to speak Arabic. The US has individuals but no military or police units who speak Arabic. Qatar’s army has fewer than 12,000 soldiers. It is hard to picture Doha providing more than 10% to a peacekeeping presence in Gaza. It is much more likely to write the necessary checks. Egypt has many more soldiers, but Cairo does not want to deploy troops in Gaza, for fear of ending up in charge there, as it was until 1967.
Using Jim Dobbins’ numbers for a heavy peace enforcement operation, Gaza would require something like 32,000 troops and 4000 police, in addition to 7500 local troops and 5500 local police. As the available local forces in Gaza would be mostly Hamas-affiliated, which Israel will not allow, the international presence will have to be beefed up accordingly.
I just don’t see how to fill that gaping hole. Are the Saudis, Emiratis, and Kuwaitis going to deploy large parts of their armies to Gaza?
The other security requirement
The third security requirement is the regional one. This need not be in the plan, but it has to be real. The US has worked hard to prevent the wider regional war, but Israel and some of Iran’s friends seem increasingly eager for one. Israel wants to move Hizbollah back from its border so that tens of thousands of civilians can return to their homes in the north. The Houthis want to demonstrate their importance in the region and gain additional aid from Iran.
The Iranians will elect a new president June 28. The Supreme Leader will retain control of foreign and security policy. But that election will likely provide some indication of the direction Tehran wants to take in the future. If the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) has its way, which seems likely, the regional situation could deteriorate quickly.
Prove me wrong
I’ll be glad to be wrong. I hope this peace plan succeeds. But I wouldn’t bet on it.
Stevenson’s army, February 4
–Houthi strikes and more NYT updates
– WSJ says US stays clear of Iran red lines
– WSJ interviews Israeli far-right leader
-NYT explains Xi’s nuclear approach
– FP says Trump would greatly change US foreign aid
-House GOP plans simple Israel aid bill
—
My SAIS colleague Charlie Stevenson distributes this almost daily news digest of foreign/defense/national security policy to “Stevenson’s army” via Googlegroups. I republish here, with occasional videos of my choice. To get Stevenson’s army by email, send a blank email (no subject or text in the body) to stevensons-army+subscribe@googlegroups.com. You’ll get an email confirming your join request. Click “Join This Group” and follow the instructions to join. Once you have joined, you can adjust your email delivery preferences (if you want every email or a digest of the emails).




 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts
